Foundation
My Definition of Universal Design and Technology
Instructional Design and Technology encompasses the study and development of human learning through both organic means and technological advancements. It is dedicated to advancing education ethically and systematically by applying theories and research to enhance learning outcomes and performance. This involves the design, management, and implementation of instructional processes and systems, with a focus on inclusive, accessible education for all learners.
As human and Ai learning continues to evolve, the integration of artificial intelligence offers unprecedented opportunities for growth. The collaboration between human expertise and AI technologies creates new pathways to enrich learning experiences, personalize education, and foster lifelong learning. Through these advancements, IDT supports the progression toward a more inclusive and adaptive educational landscape.
History of Instructional Design and Technology
I hadn’t thought of technology as fire, the wheel, or smelting, and the development of parts becoming the pathway for computers and IDT, all pivotal moments to develop parts of a whole. Today we have intelligence housed in computers and robotics; its distant cousin being the printing press.
In the 1940’s World War II advanced learning strategies, Division of Visual Aids for War Training. This employed the use of films, manuals, videos, and learning curriculum via overhead projectors, audio equipment, simulators and training devices to assist in memory and retention of materials. Shannon and Weaver (1949) developed a model of communication focusing on all aspects of communication, sender, receive, and channel or medium in which it was sent. The process is emphasized over the media. (Reiser, 2017) Gagne, Briggs, and Flannagan among others were employed to develop new techniques for training and efficiency. Jean Piaget (1952) - The Origins of Intelligence in Children: Introduced cognitive development stages (sensorimotor, preoperational, concrete operational, formal operational).
Image Credit: Science & Behavior 2024
After the war was over the field of research continued. Skinner (1958) stated that programmed instructional materials should present instructions in small steps, require active responses to frequent questions, provide immediate feedback and allow for learner self-pacing. Data regarding the effectiveness of the materials were collected, instructional weaknesses were identified, and the materials were revised accordingly. The trial and revision formula would be equivalent to formative evaluation. The steps in Behaviorism were to write the objective with desired behavior, the conditions under which they were to be performed, and criteria with which they are to be judged (Mager 1984). A criterion Referenced Testing method refers to how well a learner performs, irrespective of how well others do, to assess entry level behaviors and to determine the success of the learning that the program was designed to teach. Formative evaluation was discovered to be an effective tool for testing out materials while being taught. Summative assessments were developed to evaluate overall performance (Cronbach, 1963).
In 1968 Audio Visual Communication: It was more conceptual and tactile in regard to design and message. The physical means in which instruction was presented to learners via films, pictures, slides.
In 1977 Educational Technology: It the focus became more theory based, discovering clarity and systems for development in all aspects of human learning.Instructional technology should be viewed as a way of looking at instructional problems, or application of science to instructional practices, the use of human and non-human resources for instructional purposes.
1980’s, technology advanced and personal computer based instructions was introduced. The design field evolved to encompass not only education, but training for enhanced job performance, which further encompassed constructivists learning tasks related to the real world learning and performance.
in 1985 Gagne developed Domains of Learning, Events of Instruction, and Hierarchical Analysis, in which there are five learning outcomes: verbal information, intellectual skills, attitudes, and cognitive strategies, and each required conditions for learning. He also developed Nine Events of Instruction. Students learn skills in order and should master the adjacent skill before moving on (Gagne, 1985).
In 1994 Instructional Technology: Incorporation of complexity: ethics, concept, theory, and advancements in technology were being integrated and refined impacting research and learning, and the incorporation of cognitive and constructivist theories.
In 2008 Incorporated all of the above while adding parameters for further evolving technological, ethical practice in learning, improving performance by creating, using, and managing tech processes and resources. (Reiser, 2017)
In 2020 the pandemic magnified the need for quality instructional design. With the accelerated use of Ai and social media, designers navigated these new technologies, learning new skills.
In 2023, and similar to 2008, IDT incorporated all of the above while adding parameters for evolving technological and theoretical advancements, and a need for ethical foundations. It also focused on learning experiences and environments, which included a variety of inputs, outputs, instructional and non-instructional designs.
Key Scholars
Adult: Does the moon move or not?
Child
(age 7): When we go, it goes.
Adult: What makes it move?
Child: We do.
Adult: How?
Child: When we walk. It goes by itself.
Image Credit: Ben Martin/Getty Images
Lev Vygotsky
Image Credit: pedagogy4change.org
Lev Vygotsky (1896-1934) was part of a group of revolutionary scholars who were working at the beginning of the twentieth century to create a new school of Soviet psychology. Vygotsky himself produced an impressive corpus of works in the span of his short lifetime. He is credited with establishing the foundation of cultural psychology and cultural-historical theory, which emphasised that human change and development, particularly the development of our thinking, is influenced by society and culture. (Hargraves, V 2021)
Vygotsky's Sociocultural Theory
Core Idea: Vygotsky proposed that social interaction is essential for cognitive development. Learning is embedded in a learner's cultural and social context and occurs through scaffolding by a more knowledgeable other.
🔹 Key Principles:
Zone of Proximal Development (ZPD): The space between what learners can do on their own and what they can do with assistance.
Scaffolding: Support provided by teachers, mentors, or peers to help learners achieve tasks within their ZPD.
Social Interaction: Collaborative experiences are vital to learning.
Cultural Context: Learning is deeply tied to cultural norms, tools, and shared
practices.
We gained a great deal from the explorations of Vygotsky. He developed the foundation for our use of Funds of Knowledge, getting to know our students through social and personal preferences. Developing relationships builds investment. We use scaffolding in the classroom as a staple for differentiated instruction, which parallels Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development. He believed in performance before competence, where students performed the skill under guidance. This would fit the needs of many learners, scaling their learning through moderated tasks, discovering where successes and error occur, eliminating repeated mistakes being ingrained and needing to be retaught. Mentoring students is one way to teach skills. Through my own journey in learning and teaching, I have realized the value for both human and artificial mentors.
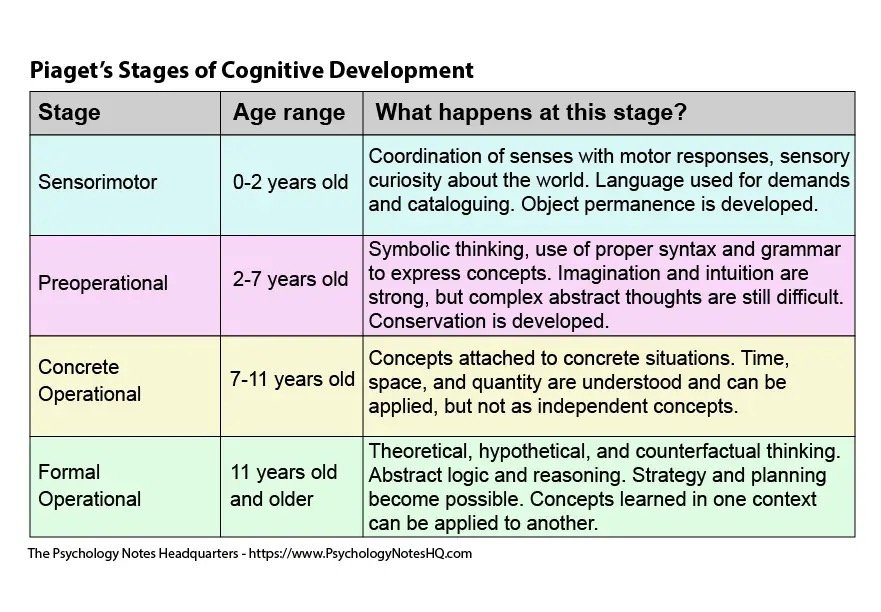
Jean Piaget
Through age and the brain's capability to understand and conceptualize, Piaget’s theory of stages gives designers insight into what needs to be taught at certain developmental stages. “Jean Piaget tried to trace specific stages in children’s progressive use of symbols and concepts to manipulate their environment. According to Piaget, two of the four stages of cognitive development occur during childhood: the preoperational stage (2 to 7 years), in which the child learns to manipulate the environment by means of symbolic thought and language; and the concrete-operational stage (7 to 12 years), in which the beginnings of logic appear in the form of classifications of ideas and an understanding of time and number. An important structure in Piaget’s theory of cognitivedevelopment is the operation, which is a cognitive structure that the child uses to transform, or “operate on,” information.” (Kagan, J 2024)
Paiget took the higher order functioning of adults as the central premise to be explained and wanted to know how an adult acquired the ability to think logically and to draw valid conclusions about the world from evidence. Piaget observed that children evolved through cycles and stages to arrive at adulthood.
Piaget believed that the stages of development were fluid and that they could happen simultaneously. (DeVries, R. 2000) This makes me think of Gardners theory of Multi Model Learners. I can tie the two together for dynamism.
Image Credit: http://www.recnv.com
https://helpfulprofessor.com
Dave Cormier - “Building a Better rhizome”
Rhiizomatic Learning Theory
Rhizomatic learning, inspired by Deleuze and Guattari's concept of the rhizome, emphasizes non-linear, connected, and decentralized learning. The metaphor of a rhizome (a type of underground plant system that spreads horizontally) is used to represent the interconnected nature of knowledge and learning pathways. Cromier has applied this theory to teaching.
Photo Credit: Dave’s Educational Blog
Key Principles of Rhizomatic Learning:
Non-linear pathways: Learning isn't a straight line; it's exploration, experimentation, and multiple routes.
Personalized and emergent knowledge: Every learner builds their unique understanding based on their experiences and explorations.
Networks over hierarchies: Rhizomatic learning focuses on collaboration, peer interactions, and building shared knowledge networks rather than strictly following teacher-led instruction.
Complexity & adaptation: Embraces uncertainty and allows for multiple interpretations and solutions.
“You can find hundreds of articles that say Learning Styles are ‘true’ and hundreds that claim the opposite. You can hear that direct instruction is better or that project based learning is better… SCIENTIFICALLY. It’s all ‘better learning’.”
Rather, Cormier believes in a holistic approach to learning. He says he values engagement over rote memory. (Cormier, D. 2024)
This theory is founded on the principle that disparate ideas combine to form deep learning. It is like the rhizome that continues to grow and branch out under the ground growing new nodes. Rhizomatic Theory and Artificial Intelligence, where the premise of learning is interdisciplinary, this could foster teaching in a very different focus than the traditional way of learning. I think in the age of tech this is such a pivotal philosophy. It fosters learning as the premise, and coupled with Ai, could be direct instruction while also being an exploratory process.
“Being relevant as a human, finding connections and building a relationship with learners and creating more involved learning will be the philosophy that enables all of us to evolve now and in the future.” (Rimban, 2024)
Learning Theories
There are many pieces to a very large puzzle in the sea of learning theories. I feel that I align with Vigotsky perspectives in teaching and learning, that relationships emerge and develop, fostering students intrinsic motivation given the right environment. A safe space for learning and curiosity is a foundation for a growth mindset, where in the quiet calm, the flow state can occur. Applying Vygotsky’s Zone of Proximal Development, the space out of time, that can be discovered and developed within the act of making art, carries over to become an asset and skill for interdisciplinary learning. Combining environment, people in the know, and meeting learners where they are in their development of personal skill sets is fulfilling for both learner and teacher. We do not live in a vacuum, but gain knowledge from one another. Constructivism, where students learn from their surroundings, socio-emotional influences and cultural linguistics, influences the learner affecting their engagement. It fosters collaboration, and incorporates the more knowledgable other, where each learning experience is a building block evolving from prior knowledge. I feel feel that there is a kernel of intrinsic understanding that exists prior to, and fosters, the fundamental stages of growth. There is always a spark, and to engage the spark increases overall curiosity that can surpass basic structural developmental stages. Integrating Piaget’s schemas into the framework, through scaffolding and differentiated teaching strategies, evolves increased capability and active learning (DeVries, R. 2000)
Howard Gardner’s Theory of Multiple Intelligences adds another element for adapting. I feel like this philosophy fosters interdisciplinary learning collaboratively. Gardner theorized that humans are Multimodal Learners and that people have unique strengths and abilities. Eric Ericsson’s Stages of PsychoSocial Development, the need to resolve conflicts within our own understanding, complement a host of learning theories. Designing with intention, understanding that all learners go through a variety of stages, house diverse talents, and possess diverse learning abilities, is inspiration for designing emmersive learning activities that are accessible to everyone. My idea of deep learning is a synthesis of information learned in a web of possibilities, of diverse paths, to ascend and land on the same space, experiencing unified deep understanding.
Lilly of the Valley (Rhizomes) Beautiful and Expansive (My Backyard)
Instructional Design Trends
The general significant trends in the IT field in our current era and the influence they will have on the future of the IT field:
There are infinite possibilities and capabilities that are on the horizon. I have spent a great deal of time researching and listening to philosophers and scientists, taking notes; dabling in what understanding I can squeeze out of the field of quantum physics, robotics and biomechanics, because these are weighty subjects. I feel that technology is something we have to embrace and find balance with. I asked Claude Sonnet 3.5 what the future will look like. These are several evolving areas affecting the future of IDT:
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Cloud Computing - More manageable ways to deal with data.
Internet of Things- Connecting more devices and generating vast amounts of data. Smarter cities, more efficient industries and more challenges in data and security.
Cybersecurity 5G and Advanced Networking
Quantum Computing
Extended Reality XR AR VR and MR
Low Code No Code Development
Green IT and Sustainability
Skill demand: Continuous skill updating, emphasis on AI, cybersecurity, and cloud technologies.
Ethical considerations: Increasing importance as technology becomes more pervasive and powerful.
Interdisciplinary approach: IT intersecting with other fields, requiring broader knowledge bases.
Focus on data: Critical importance of data management, analysis, and protection.
User experience: Greater emphasis on creating intuitive, user-friendly interfaces. (Claude, 2024)
In direct relation to IDT, I feel like it is important for humans to diversify skill sets. We have to add to our knowledge and continue to be innovative and adaptable. It is our instincts and intuition, the thing that makes us human, that will be our best asset and will be needed in IDT field. I feel like the combination of capabilities of humans and the advancing intelligence of Ai is a very strong collaboration.
ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
Partnering with artificial intelligence, strategically employed within the design of educational frameworks, provides enhanced learning. Set parameters and guidelines should be employed, scaffolding learners in higher order thinking through questioning, assisted strategic learning, and use of frameworks based on design using SMART Goals: scalable, measurable, achievable, relevant and time bound instructional strategies. In my own learning and design, I continue to evolve in this way, with explicit instructions for Ai not to provide answers, but to question my thought processes and encourage growth in understanding through conversations, rapid fire questioning just beyond my reach with a touch of struggle, have enhanced my learning and understanding. This aligns with Connectivism, an emerging learning theory in our digital age, where knowledge acquisition occurs through engagement with others and information systems. In this case, understanding exists through connections, both in the mind and across technological networks. Relying on collaboration, with emphasis on creating and maintaining knowledge, while adapting to rapidly changing technology, is a skill to be immersed in. (Refer to Connectivism)
“By creating a learning environment that values individual exploration and the natural creation of connections and knowledge, students may be better equipped to engage with the complex and rapidly changing landscape of AI. This approach may also help to create a more equitable and inclusive learning environment, by allowing each student to bring their unique knowledge and experiences to the process of learning”.(Rimban, 2023)
CANVA
Canva is a great platform for Instructional Design. My students' created Zines, a DIY book project in relation to self and art. This project incorporated handmade and Ai generated artwork, used technology, and SEL for personal development though individual creations and collaborative projects. This provided space to expand interpersonal relationships, where students participated in giving and receiving feedback; It also enhanced skills in reading, writing, technological aptitude, by using a variety of multi-step techniques for creating traditional and digital artwork. This lesson incorporated technology, direct instruction, traditional tactile skills, and Ai. This applied strategy embodies Connectivism through exploration and integration of human and Ai driven learning platforms. (Pedroso, J. 2023)(Refer to Connectivism and Constructivism)
GAMIFICATION: MINECRAFT EDUCATION EDITION
Designers can utilize this platform for interactive engagement in an array of subjects. This edition of Minecraft incorporates a fun environment that invites learners to engage in open ended educational activities and provides opportunities to practice specific skills in a low-stakes environment, internalizing information and deep learning through exploration. This platform integrates multimodal learning: logic, spacial awareness, time management, critical thinking, math, reading, and spans the developmental stages through creative problem solving. Knowledge acquisition and joint learning influences interaction and scaffolds interpersonal development and relationship building activities in group play. With continually evolving information and technological advancements, in a sandbox environment, free to roam build and learn in an educational environment magnifies the future of human and Ai integration elevating gaming in mainstream instructional design. (Alawajee, O. 2021) (Refer to Constructivism, Connectivism, & Rhizomatic Learning Theory)
My Philosophy
Education: Teaching & Learning
-On teaching art and Perspective: My brain immediately thinks of the cosmos and I see a vast sea of constellations and quantum physics (to the degree I understand). Not only is perspective a fundamental design principle, but an abstract concept like individual understanding of oneself in relation to the universe and also others. Perspective in relationship to learning, compared to converging and diverging lines, is a distant place that can be close to, and far away from, our purposeful destination. -
Simple to complex, deep learning is an investment from the onset through visual imagery, words, and social interaction, among a host of other things. Assessments gauge needs, and develop intrinsic motivation and space to house permanent knowledge. It is important to teach with engagement and curiosity by authentically adapting to the needs of the students. I have invested a great deal of time in learning art, teaching, and delving into Instructional Design and Technology. Passing on mastery of craft through teaching engages learners. They evolve and the subject matter embeds in their own paradigm creating new meaning. I design with learners interests in mind, and through differentiation, drawing on their individual pathways, teaching them how to connect, think, and apply abstract and seemingly disparate concepts at their level of ability and comprehension, and then extend it further. Interconnectivity is essential for deep understanding. Activating high level processing for students critical thinking and problem solving skills creates connection, revealing to themselves, their own vast capabilities. Collaboration, integrating understanding with others, develops conceptual blending of information. Interwoven learning theories enhance the learning experience and creates a vehicle for new neural pathways. Individual interest, connected to new concepts, fostered through academics and socio-emotional learning, builds a healthy relationship to experiences making them relevant and meaningful.
Education & Technologies
By getting to know the needs of learners, including myself as curious seeker, understanding of new subject matter, the nature of IDT fosters a continuous evolving platform that adapts to the ever changing nature of human learning and technology. This fluidly promotes a well rounded, and naturally incorporates, interdisciplinary methods for designing for a vast array of multimodal and diverse learners. Infinite feedback loops, continually studying current trends in technology, learning curriculum and design methods, and further developing my relationship with technology and artificial intelligence informs decisions. Ai enhances my understanding of possibilities, and the information that I have garnered inevitably spills over to my design and teaching. The inclusion of technology enables students to learn at their own pace. Teachers and agents working together will be a building block for Connectivism, enabling understanding for students in the moment, where they are at and what they need for further understanding, and then transfer skills to interdisciplinary studies. Technology and artificial intelligence will change the nature and trajectory of education, and enhance and change the nature of the traditional learning environment. Skills for use and understanding need to be taught and built into the curriculum. Co-creating with Ai will benefit the designer, teacher and student, where working together extends our abilities, and includes the best of humans and technological assets combined.
References
Alawajee, O., & Delafield-Butt, J. (2021). Minecraft in education benefits learning and social engagement. International Journal of
Game-Based Learning, 11(4), 19-56.
Cormier, D. (2024). Dave Cormier's edblog. Retrieved December 8, 2024, from https://davecormier.com/edblog/
Gagné, R. M. (1985). The Conditions of Learning. New York: Holt, Rinehart, and Winston.
Hargraves, V. (2021, March 17). Vygotsky’s philosophy of education. The Education Hub. Retrieved December 8, 2024, from
https://theeducationhub.org.nz/vygotskys-philosophy-of-education/
DeVries, R. (2000). Vygostky, Piaget and education: A reciprocal assimilation of theories and educational practices. New
Ideas in Psychology, 18, 187-213.
Flavian, H. (2019). Mediation and thinking development in schools: Theories and practices for educators. Emerald Publishing
Ltd.
Moll, L. (2014). L. S. Vygotsky and education. Routledge.
Moore, A. (2012). Teaching and learning: Pedagogy, curriculum and culture. Routledge.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1978). Mind in society: The development of higher psychological processes. Cambridge, MA: Harvard
University Press.
Vygotsky, L. S. (1934/1986). Thought and language. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Kagan, J. , Lerner, . Richard M. and Bornstein, . Marc H. (2024, October 3). human behaviour. Encyclopedia Britannica.
https://www.britannica.com/topic/human-behavior
Mager, R. F. (1984). Preparing Instructional Objectives. Center for Effective Performance.
Muljana, A., & Luo, H. (2023). Social media platforms' role in professional learning and instructional design. Educational Technology
& Research Journal, 65(3), 251–267. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1398265
Pedroso, John Erwin & Sulleza, Rv & Francisco, Keith Hae Moon & Noman, Ayya Jade & Martinez, Chynna Althea. (2023).
Students’ Views on Using Canva as an All-In-One Tool for Creativity and Collaboration. JOURNAL OF DIGITAL LEARNING AND
DISTANCE EDUCATION. 2. 443-461. 10.56778/jdlde.v2i1.117.
Reiser, R. A. (2017). A History of Instructional Design and Technology. Educational Technology Publications.
Rimban, Erwin, Rhizomatic Pedagogy In The Age Of Artificial Intelligence (February 22, 2024). Available at SSRN:
https://ssrn.com/abstract=4734793 or http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4734793
Shannon, C. E., & Weaver, W. (1949). The Mathematical Theory of Communication. University of Illinois Press.
Skinner, B. F. (1958). The Behavior of Organisms: An Experimental Analysis. Appleton-Century-Crofts.
Tulsiani, R. (2024, January 6). The future impact of AI on eLearning. eLearning Industry.
https://elearningindustry.com/the-future-impact- of-ai-on-elearning
Wardlow, L. (2014). The Philosophies of Learning Behind Improving Access to Learning Resources. Pearson Research and Innovation
Network. 20 July 2016, from https://www.pearsoned.com/wp-content/uploads/DigitalAge_AccessReport_021714.pdf